Generative Engine Optimization (GEO)
Navigating the Future of Search in the Age of AI
As generative AI tools like ChatGPT, Google's Search Generative Experience (SGE), Perplexity, and others rapidly change how users discover and consume information, businesses are facing a pivotal moment. Traditional search engine optimization (SEO) is no longer the sole path to digital visibility. Instead, a new discipline—Generative Engine Optimization (GEO), also known as Generative Search Optimization (GSO)—is emerging to help brands appear in AI-generated answers and conversational interfaces. But is it wise to rush headlong into GEO, or is there a more strategic, sustainable approach?
This article explores what GEO is, how it differs from SEO, its applications across industries, best practices, measurement strategies, and what the future holds for search in the era of generative AI.
Why GEO/GSO Is Emerging Now
The rise of generative AI has fundamentally altered user search behavior. Instead of sifting through pages of blue links, users increasingly expect direct, synthesized answers from AI-powered assistants and search engines. According to Gartner, by 2026, 25% of all searches are projected to take place via AI interfaces. This shift is driving businesses to rethink their digital strategies—not just to rank in traditional search, but to be cited, recommended, or paraphrased by AI systems.
Recent research highlights the scale of this transformation:
- 63% of marketers are incorporating GSO into their 2024 strategies.
- 78% of businesses in a Storyblock survey have adjusted their content marketing approach to align with AI-driven search engines.
- Presence of AI Overview is correlated with a 34.5% lower average CTR.
GSO vs. GEO: Clarifying the Relationship
Generative Search Optimization (GSO) and Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) are closely related concepts, often used interchangeably. Both refer to optimizing digital content so that it is discoverable, understandable, and referenceable by AI-powered search engines and chatbots. While GSO is sometimes used as a broader term encompassing all generative search interfaces, GEO typically focuses on the specific mechanisms by which AI engines select and synthesize content for their responses.
Key takeaway: Whether you call it GSO or GEO, the goal is the same: ensure your content is surfaced, cited, or recommended in AI-generated answers, not just in traditional search results.
How GEO Works
GEO involves understanding how AI models retrieve, interpret, and synthesize information:
- Data Ingestion: AI engines pull from structured data (schema markup), indexed web content, and authoritative sources.
- Contextual Synthesis: Responses are generated based on the user's query, previous interactions, and system instructions, often producing a single, highly relevant answer.
- Personalization: AI models may tailor responses based on user context, preferences, and conversational history.
This creates a nuanced optimization landscape. Unlike traditional SEO, where ranking factors are relatively transparent, GEO requires a deep understanding of how different AI models process and prioritize information.
Traditional SEO vs. GEO: A Comparative Overview
Both SEO and GEO aim to increase brand and content visibility, but they differ in approach, optimization focus, and measurement.
Nuances in GEO Optimization:
- Answer Quality: Content must be clear, concise, and directly answer likely user queries.
- Platform Tailoring: Strategies may vary for ChatGPT, Bing, Perplexity, and others.
- Structured Data: Schema markup (FAQ, Product, HowTo) is critical for AI parsing.
- Authority Signals: E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) remains vital.
Industry Sentiment and Adoption: Hype, Skepticism, and Caution
The rapid adoption of GEO/GSO has sparked both enthusiasm and skepticism within the marketing community:
- Adoption Rates: As noted, 63% of marketers are integrating GSO, and 71% of respondents to a McKinsey survey reported their businesses use AI for at least one work function.
- Skepticism: Many SEO professionals view GEO as an extension, not a replacement, of SEO. There are concerns about misinformation, overhyped tactics, and the ethical implications of AI scraping and content synthesis.
- Cautions: Industry leaders warn against "snake oil" shortcuts and manipulative tactics. The consensus is clear: focus on high-quality, structured, user-first content, and avoid chasing short-term hacks that could backfire as AI platforms evolve.
GEO Applications in B2C and B2B
B2C (E-commerce and Consumer-Facing Brands)
GEO is particularly impactful in e-commerce and consumer research:
- Product Discovery: AI assistants increasingly recommend products in response to queries like "best running shoes" or "top laptops under $1000."
- Optimization Tactics:
- Structured Product Data: Implement schema markup (Product, Review, FAQ) to help AI engines understand and surface your offerings.
- Leverage Reviews: Encourage and aggregate positive reviews to influence AI-generated recommendations.
- Content Quality: Create detailed, up-to-date product descriptions and comparison guides.
- Example: An online retailer uses FAQ schema and structured product data to ensure their products are cited in Perplexity AI's shopping recommendations.
B2B (Business-Focused and Technical Brands)
For B2B organizations, GEO opens new avenues for visibility:
- Technical Answers: Ensure your documentation and technical resources are accessible and structured for AI parsing.
- Vendor Shortlists: Publish high-authority thought leadership and case studies to appear in AI-generated vendor recommendations.
- Authority Building: Secure backlinks from reputable industry sources and maintain a robust presence on platforms like Wikipedia.
- Example: A B2B SaaS company leverages Wikipedia entries and authoritative backlinks to appear in ChatGPT's top software recommendations.
Other Potential Applications for GEO
1. B2B SaaS Success
A SaaS provider noticed increased citations in ChatGPT's software recommendations after enhancing their Wikipedia presence and securing high-authority backlinks. This led to a measurable uplift in branded search queries and demo requests.
2. E-commerce Optimization
An online retailer implemented FAQ schema and engaged with relevant subreddits. As a result, their products began appearing in Perplexity AI's answers for "best budget headphones," driving a spike in referral traffic from AI interfaces.
3. Publisher Adaptation
A major publisher initially saw a traffic drop as AI-generated answers replaced traditional clicks. By adopting GSO best practices—improving structured summaries and monitoring AI mentions—they regained visibility and stabilized their referral traffic.
4. Consultancy Firm Experiment
A consultancy ran prompt testing across multiple AI platforms, refining their content structure and summaries. This proactive approach increased their inclusion in AI-generated business advice and vendor shortlists.
GEO Best Practices: Actionable Recommendations
To succeed in the evolving search landscape, businesses should adopt the following GEO best practices:
- Maintain SEO Fundamentals
- Ensure your site is fast, crawlable, and user-friendly.
- Continue optimizing for traditional search as a foundation.
- Use Structured Data and Schema Markup
- Implement schema types such as FAQ, Product, HowTo, and Review.
- Structured data helps AI engines parse and understand your content.
- Boost E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness)
- Build authority through high-quality content, reputable backlinks, and expert authorship.
- Maintain a consistent brand presence across platforms (website, Wikipedia, industry directories).
- Monitor AI Mentions and Test Prompts
- Regularly test your brand and product queries on AI platforms like ChatGPT, Bing, and Perplexity.
- Track when and how your content is cited or referenced.
- Tailor Strategies by Platform
- Understand the nuances of each AI engine—what data sources they use, how they synthesize answers, and their citation practices.
- Adjust content and structure accordingly.
- Avoid Manipulative Tactics
- Steer clear of keyword stuffing, fake reviews, or attempts to "game" AI models.
- Focus on genuine value and user-first content.
- Stay Updated on AI Developments
- Monitor platform updates, new AI tools, and changes in how AI engines source and display information.
- Participate in industry forums and follow thought leaders for the latest insights.
Measuring the Impact of GEO Initiatives
Measuring GEO effectiveness requires new metrics and tools beyond traditional SEO analytics:
What to Measure
- AI Citations and Mentions: Track when your brand or content is referenced in AI-generated answers.
- Brand Visibility: Monitor branded search volume and presence in AI recommendations.
- Traffic Referrals: Use analytics to identify referral traffic from AI platforms (where possible).
- Branded Traffic Uplift: Compare changes in branded search queries before and after GEO initiatives.
- Conversions and Revenue Attribution: Tie AI-driven traffic to conversions and revenue, using UTM parameters or custom landing pages.
- AI Impression Share and Assistant Referrals: Emerging KPIs that track how often your content appears in AI answers and is recommended by digital assistants.
How to Measure
- Prompt Testing: Regularly input relevant queries into AI platforms to observe if and how your content appears.
- AI Visibility Tools: Leverage emerging tools designed to monitor AI citations and mentions (e.g., some features in Ahrefs, Semrush).
- Log File Analysis: Analyze server logs for referral patterns from AI interfaces.
- Manual Tracking: Maintain a database of observed AI citations and monitor changes over time.
I have been working on AirOps workflows to automate repetitive SEO tasks. This got me thinking, could I create a workflow to query AI models? So, I got to work. I created a workflow that queries ChatGPT, Claude, Perplexity, and Gemini on Monday, Wednesday, Friday, and Sunday, twice per day.
The input prompts are pulled from a Grid:
The outputs are written on the same Grid, on a separate sheet:
You can then use the data to create dashboards on Looker Studio. For example, you can see the share of your site's citations over time for specific prompts/ queries:
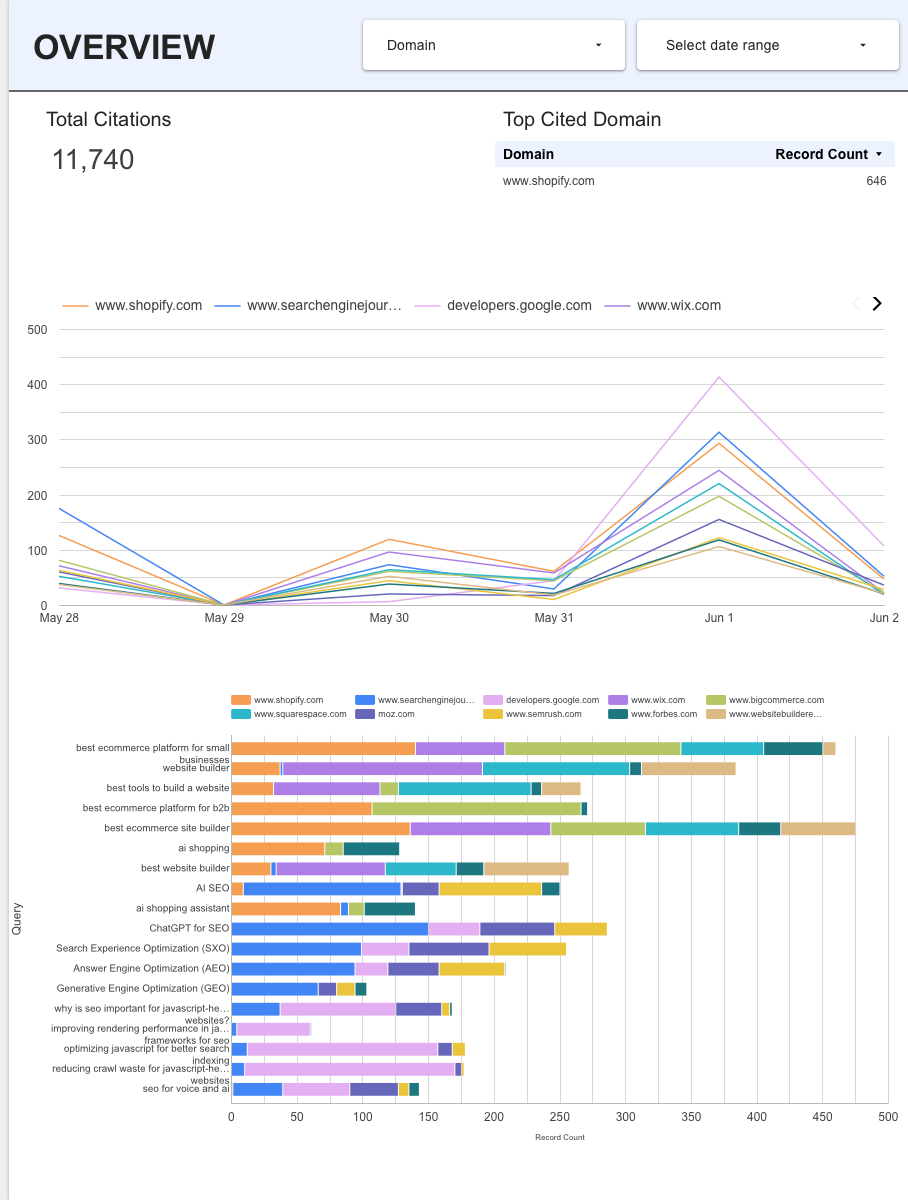
Or you can use your data to calculate a visibility score for topics of interest:
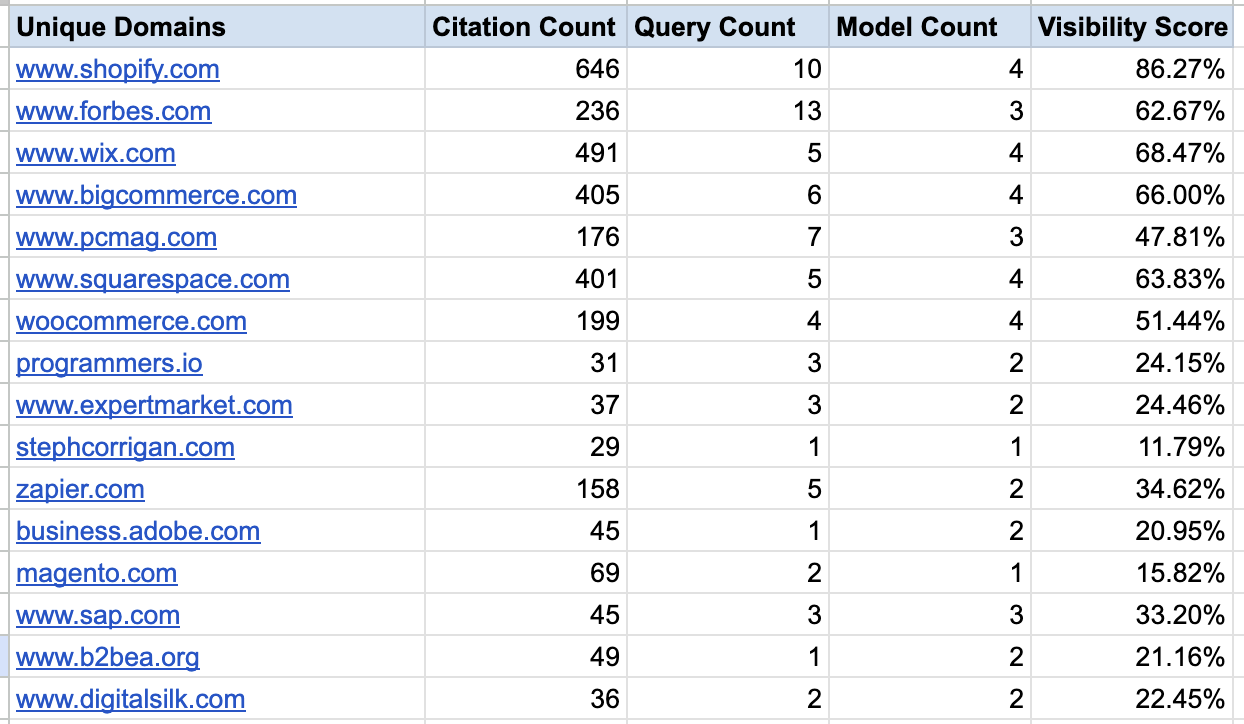
You can try the workflow here:
Challenges
- Limited Transparency: AI platforms may not always cite sources or provide referral data.
- Rapid Evolution: Tools and best practices are evolving; staying agile is essential.
- Attribution Complexity: Connecting AI-driven visibility to conversions can be challenging due to "zero-click" answers.
The Future of Search with GEO
The search landscape is poised for dramatic change as generative AI becomes mainstream:
- AI-Driven Search Growth: By 2026, 25% of searches are expected to occur via AI interfaces (Gartner, via Search Engine Land).
- Zero-Click Searches: AI-generated summaries are increasing, reducing the need for users to click through to websites.
- Voice and IoT Integration: Search will extend beyond screens to voice assistants and ambient devices, making conversational GEO even more critical.
- AI-Enhanced Product Discovery: E-commerce and B2B buyers will rely on AI recommendations for product research and vendor selection.
- New KPIs: Metrics like AI impression share and assistant referrals will become standard for measuring digital visibility.
- Continuous Evolution: As AI models and user behaviors evolve, so too must GEO strategies—requiring ongoing learning and adaptation.
Conclusion
GEO and GSO are not replacements for SEO, but essential evolutions in a world where AI-driven search is becoming the norm. The brands that thrive will be those who:
- Align content with AI structures and schema,
- Prioritize credibility and user value,
- Monitor and adapt to emerging AI platforms,
- Avoid manipulative shortcuts in favor of sustainable, user-first strategies.
As search continues to shift toward conversational, AI-powered experiences, now is the time to future-proof your digital presence. Invest in GEO not as a fad, but as a strategic pillar—ensuring your brand remains visible, trusted, and relevant in the next era of search.